What people are missing with adding labile DOC, aka carbon dosing, is the problems it causes with corals. There's no doubt stimulating bacterial growth will consume nitrates and phosphates. However, stimulating bacterial growth in the surface mucus layers and holobionts of corals has been shown to directly lead to both chronic and acute problems. The increased availabile labile DOC allows heterotrophic microbial processes to utilize refractory DOC they would not normally be able to consume but this comes with the risk of creating anoxic conditions for corals. I feel I also need to point out turbidity isn't a reliable indicator of microbial counts, this
paper shows microbial counts can be quite high without an associated increase of trubidity
View attachment 32409357
Here's some links for those interested in reading more about the how DOC works in reef ecosystems:
"Coral Reefs in the Microbial Seas " This video compliments Rohwer's book of the same title. Used copies are available on line and it may be free to read on Internet Archive. both deal with the conflicting roles of the different types of DOC (carbon dosing) in reef ecosystems and how it can alter coral microbiomes. While there is overlap bewteen his book and the video both have information not covered by the other and together give a broader view of the complex relationships found in reef ecosystems and are an excellent starting point to understand the conflicting roles of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC, aka "carbon dosing") in reef ecosystems.
Maintenance of Coral Reef Health (refferences at the end)
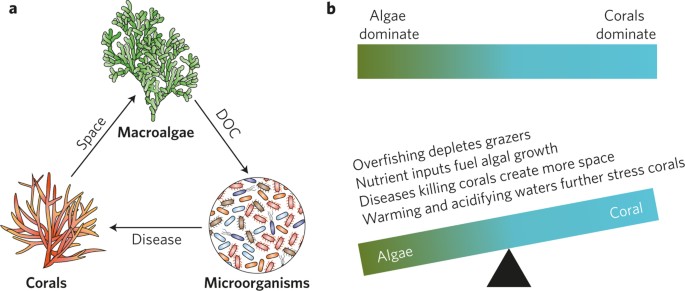
Indirect effects of algae on coral: algae‐mediated, microbe‐induced coral mortality
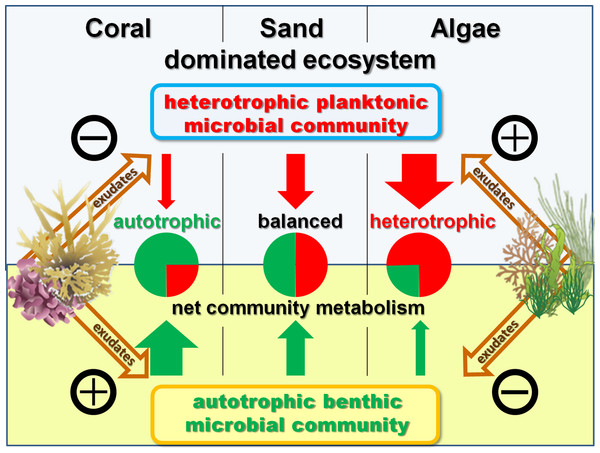
Influence of coral and algal exudates on microbially mediated reef metabolism.
Coral DOC improves oxygen (autotrophy), algae DOC reduces oxygen (heterotrophy).
Benthic primary producers in tropical reef ecosystems can alter biogeochemical cycling and microbial processes in the surrounding seawater. In order to quantify these influences, we measured rates of photosynthesis, respiration, and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) exudate release by the dominant...

peerj.com
Role of elevated organic carbon levels and microbial activity in coral mortality
Effects of Coral Reef Benthic Primary Producers on Dissolved Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity
Algae releases significantly more DOC into the water than coral.
Benthic primary producers in marine ecosystems may significantly alter biogeochemical cycling and microbial processes in their surrounding environment. To examine these interactions, we studied dissolved organic matter release by dominant benthic taxa and subsequent microbial remineralization in...

journals.plos.org
Pathologies and mortality rates caused by organic carbon and nutrient stressors in three Caribbean coral species.
DOC caused coral death but not high nitrates, phosphates or ammonium.
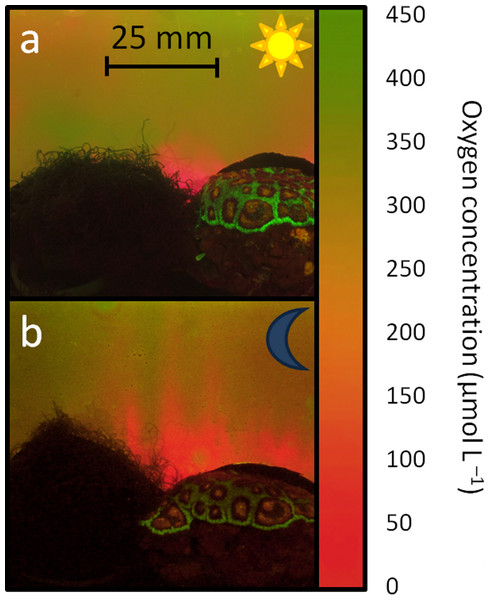
Visualization of oxygen distribution patterns caused by coral and algae
Planar optodes were used to visualize oxygen distribution patterns associated with a coral reef associated green algae (Chaetomorpha sp.) and a hermatypic coral (Favia sp.) separately, as standalone organisms, and placed in close proximity mimicking coral-algal interactions. Oxygen patterns were...

peerj.com
Biological oxygen demand optode analysis of coral reef-associated microbial communities exposed to algal exudates
Exposure to exudates derived from turf algae stimulated higher oxygen drawdown by the coral-associated bacteria.
Algae-derived dissolved organic matter has been hypothesized to induce mortality of reef building corals. One proposed killing mechanism is a zone of hypoxia created by rapidly growing microbes. To investigate this hypothesis, biological oxygen ...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Microbial ecology: Algae feed a shift on coral reefs
Human pressures on coral reefs are giving macroalgae a competitive advantage over reef-building corals. These algae support larger, and potentially pathogenic, microbial populations that are metabolically primed for less-efficient, yet faster, carbohydrate remineralization, perpetuating a...

www.nature.com
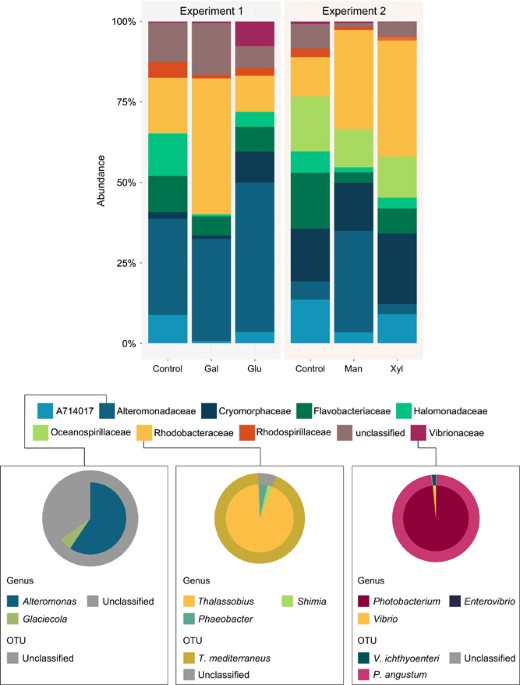
Coral and macroalgal exudates vary in neutral sugar composition and differentially enrich reef bacterioplankton lineages.
Increasing algal cover on tropical reefs worldwide may be maintained through feedbacks whereby algae outcompete coral by altering microbial activity. We hypothesized that algae and coral release compositionally distinct exudates that differentially alter bacterioplankton growth and community...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Sugar enrichment provides evidence for a role of nitrogen fixation in coral bleaching
Elevated ammonium delays the impairment of the coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis during labile carbon pollution
(here's an argument for maintaining heavy fish loads if you're carbon dosing)
Labile dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is a major pollutant in coastal marine environments affected by anthropogenic impacts, and may significantly con…

www.sciencedirect.com
Excess labile carbon promotes the expression of virulence factors in coral reef bacterioplankton
Coastal pollution and algal cover are increasing on many coral reefs, resulting in higher dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations. High DOC concentrations strongly affect microbial activity in reef waters and select for copiotrophic, often potentially virulent microbial populations. High...

www.nature.com
Unseen players shape benthic competition on coral reefs.
Recent work has shown that hydrophilic and hydrophobic organic matter (OM) from algae disrupts the function of the coral holobiont and promotes the invasion of opportunistic pathogens, leading to coral morbidity and mortality. Here we refer to these dynamics as the (3)DAM [dissolved organic...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Allelochemicals Produced by Brown Macroalgae of the Lobophora Genus Are Active against Coral Larvae and Associated Bacteria, Supporting Pathogenic Shifts to Vibrio Dominance.
Diverse microbial communities associate with coral tissues and mucus, providing important protective and nutritional services, but once disturbed, the microbial equilibrium may shift from a beneficial state to one that is detrimental or pathogenic. Macroalgae (e.g., seaweeds) can physically and...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Macroalgae decrease growth and alter microbial community structure of the reef-building coral, Porites astreoides.
With the continued and unprecedented decline of coral reefs worldwide, evaluating the factors that contribute to coral demise is of critical importance. As coral cover declines, macroalgae are becoming more common on tropical reefs. Interactions between these macroalgae and corals may alter the...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Macroalgal extracts induce bacterial assemblage shifts and sublethal tissue stress in Caribbean corals.
Benthic macroalgae can be abundant on present-day coral reefs, especially where rates of herbivory are low and/or dissolved nutrients are high. This study investigated the impact of macroalgal extracts on both coral-associated bacterial assemblages and sublethal stress response of corals. Crude...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Biophysical and physiological processes causing oxygen loss from coral reefs.
Global microbialization of coral reefs
DDAM Proven
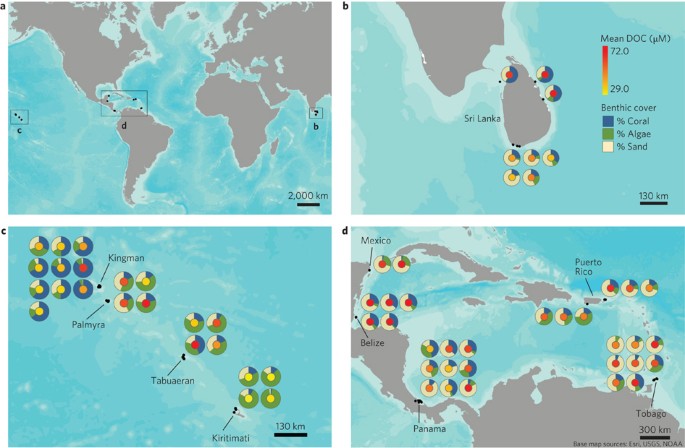
Analysis of 60 sites in three ocean basins suggests that overgrowth of fleshy algae on coral reefs supports higher microbial abundances dominated by copiotrophic, potentially pathogenic bacteria via the provision of dissolved inorganic carbon.

www.nature.com
Coral Reef Microorganisms in a Changing Climate, Fig 3
Coral reefs are one of the most diverse and productive ecosystems on the planet, yet they have suffered tremendous losses due to anthropogenic disturbances and are predicted to be one of the most adversely affected habitats under future climate ...

www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ecosystem Microbiology of Coral Reefs: Linking Genomic, Metabolomic, and Biogeochemical Dynamics from Animal Symbioses to Reefscape Processes